If a statically indeterminate structure is subjected to change in temperature, internal stresses are induced. This can be found in structures such as cooling towers and chimneys, where the internal and external temperatures are different. This implies that the temperature at the two extreme fibres of the material section are not the same and since the structure is restrained, internal stresses are developed due to thermal strain. We can use force method to obtain the magnitude of such stresses, in order to make appropriate designs.
Instead of the normal canonical equation for externally applied load, we now replace the free terms with deformation due to temperature change as shown below;
The deformation of a structure at a point due to temperature difference is given by;
Where;
α = coefficient of thermal expansion of the material
h = depth of the member
∆t = change in temperature
tav = average temperature for the member
∫M ̅ds = Area of the bending moment diagram for the member
∫N ̅ds = Area of the axial force diagram for the member
In summary, the steps to follow are:
(1) Determine the degree of redundancy in the structure, and write the appropriate canonical equation.
(2) Draw your basic or primary system as usual
(3) Obtain unit bending moment, shear, and axial force diagrams
(4) Calculate the unit displacement using Mohr’s integral or Vereschagin’s method
(5) Calculate the free terms of the canonical equation (displacement due to temperature difference)
(6) Solve the canonical equation
(7) Plot your internal stresses diagram.
SOLVED EXAMPLE
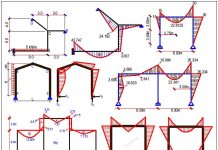
A portal frame is fixed at the column base A, and hinged at the far end of the beam C as shown above. The column of the frame has a cross-section of 30cm x 30cm while the beam has a depth of 60cm and width of 30cm. The temperature inside the frame (t1) is 50°C while the temperature outside (t2) is 21°C. Draw the bending moment, shearing force, and axial force diagram for the temperature difference action on the frame (E = 2.17 × 107 KN/m2, α = 11 × 10-6 /°C).
SOLUTION
Geometric properties and temperature data;
Moment of inertia of column IC = (bh3)/12 = (0.3 × 0.33)/12 = 6.75 × 10-4 m4
Moment of inertia of beam IB = (bh3)/12 = (0.3 × 0.63)/12 = 5.4 × 10-4 m4
We desire to work in terms of IC such that IC/IB = 0.125
Hence flexural rigidity of the column, EIC = (2.17 × 107) × (6.75 × 10-4) = 14647.5 KNm2
For the frame above;
∆t = t2 – t1 = 50 – 21 = 29°C; tav = (50 + 21)/2 = 35.5°C
For member AB, ∆t/h = 29/0.3 = 96.667; For member BC, ∆t/h = 29/0.6 = 48.333
Basic system
The next step in the analysis is to reduce the structure to a basic system, which is a system that must be statically determinate and stable. The frame is statically indeterminate to the second order, which means that are we are going to remove two redundant supports.
Degree of static indeterminacy is given by;
RD = (3m + r) – 3n – s ————————— (2)
So that RD = (3 × 2) + 5 – (3 × 3) – 0 = 2
By choice, I am deciding to remove the two reactive forces at support C of the frame to obtain the basic system as shown below;
Analysis of case 1; X1 = 1.0, X2 = 0
The simple static analysis of the structure loaded with case 1 loading is as shown below in terms of the internal stresses diagram.
Analysis of case 2; X1 = 0, X2 = 1.0
The simple static analysis of the structure loaded with case 1 loading is as shown below in terms of the internal stresses diagram.
The appropriate canonical equation for this structure is therefore;
δ11X1 + δ12X2 + Δ1t = 0
δ21X1 + δ22X2 + Δ2t = 0
Computation of the influence coefficients
Influence coefficients are based on Mohr’s integral such that δi = 1/EI ∫Mmds. When we wish to handle this by using the graphical method (making use bending moment diagrams), we directly employ Verecshagin’s rule which simply states that when we are combining two diagrams of which one must be of a linear form (due to the unit load) and the other of any other form, the equivalent of Mohr’s integral is given by the area of the principal combiner multiplied by the ordinate which its centroid makes with the linear diagram. The rule can also work vice versa. This process has been adopted in this work.
δ11 (Deformation at point 1 due to unit load at point 1)
This is obtained by the bending moment of case 1 combining with itself. This is shown below.
δ11 = (5 × 5 × 4) + (1/3 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 0.125) = 105.208
δ21 = δ12 (Deformation at point 2 due to unit load at point 1 which is equal to deformation at point 1 due to unit load at point 2 based on Maxwell’s theorem and Betti’s law)
This is obtained by the bending moment diagram of case 1 combining with bending moment diagram of case 2. This is shown below.
δ21 = (1/2 × 5 × 4 × 4) = 40
δ22 (Deformation at point 2 due to unit load at point 2)
This is obtained by the bending moment diagram of case 2 combining with itself. This is shown below.
δ22 = (1/3 × 4 × 4 × 4) = 21.333
Influence coefficients due to temperature difference
Case 1 (Take a good look at the bending moment and axial force diagrams)
Δ1t/EIC = α∆t/h ∫M ̅ds + αtav ∫N ̅ds
Considering the first term of the equation for members AB and BC = [(11 × 10-6 × 96.667 × 5 × 4) + (11 × 10-6 × 48.333 × (1/2) × 5 × 4)] = 0.02791
Considering the second term of the equation for member AB = (11 × 10-6 × 35.5 × 1 × 4) = 0.001562
Hence, Δ1t = α∆t/h ∫M ̅ds + αtav ∫N ̅ds = 0.02791 + 0.001562 = 0.029473EIC
Δ1t = 0.029473 × 14647.5 = 431.691
Case 2 (Take a good look at the bending moment and axial force diagrams)
Δ2t/EIC = α∆t/h ∫M ̅ds + αtav ∫N ̅ds
Considering the first term of the equation for members AB = (11 × 10-6 × 96.667 × (1/2) × 4 × 4) = 0.0085067
Considering the second term of the equation for member BC = (11 × 10-6 × 35.5 × -1 × 5) = -0.0019525
Hence, Δ2t = α∆t/h ∫M ̅ds + αtav ∫N ̅ds = 0.0085067 – 0.0019525 = 0.0065542EIC
Δ2t = 0.0065542 × 14647.5 = 96.0026
The appropriate canonical equation now becomes;
105.208X1 + 40X2 = -431.691
40X1 + 21.333X2 = -96.0026
On solving the equations simultaneously; X1 = -8.332 KN; X2 = 11.122 KN
The final value of the internal stresses is given by the equations below;
Mdef = M1X1 + M2X2
Qdef = Q1X1 + Q2X2
Ndef = N1X1 + N2X2
Final Moment (Mdef)
MA = (-8.332 × 5) + (11.122 ×4) = 2.828 KNm
MB = (-8.332 × 5) = -41.660 KNm
MC = hinged support = 0
Final Shear Force (Qdef)
QA – QBB = (11.122 × -1) = -11.122 KN
QBR – QCL = (-8.332 × 1) = -8.332 KN
Final Axial Force (Ndef)
NA – NBB = (-8.332 × 1) = -8.332 KN
NBR – NCL = (11.122 × -1) = -11.122 KN
Thank you visiting, and remember to like our facebook page at
www.facebook.com/structville