As the name implies, signposts are post bearing structures that offer information or guidance to people. They are a prominent feature of our highways, streets, city centers, villages, and areas of public gathering. Signposts are usually placed strategically away from obstruction as they are intended to show information like route direction, warnings, route assurance, traffic signs, commercial advertisements, etc.

EN 12899-1:2007 requires that signposts made of steel structures should conform with EN 1993-1-1:2005 (Eurocode 3). One of the major concerns in the design of billboards and signposts is the risk of failure under wind load, which has serious economic and safety consequences. A failed highway sign structure can cause injury to pedestrians, damage vehicles, and obstruct traffic. As a result, such structures that are exposed to the public must satisfy all needed safety considerations. Additional risks of vehicles colliding with sign structures should also be checked, with passive protection provided for such structures.
Actions on Sign Structures
Wind action on signposts and billboards can be evaluated according to EN 1991-1-4:2005 (Eurocode 1 Part 4). ASCE 7-10 code of practice can also be used for the evaluation of wind load on sign structures. The National Annex to BS EN 12899-1:2007 recommends suitable wind loads for the majority of signs in the UK. Whilst is it more conservative than performing a full analysis, it is simpler and quicker.
Other forces that may need to be taken into account when designing sign structures are point loads and dynamic snow load (not applicable in Nigeria). The UK National Annex recommends that signs should be able to withstand a force of 0.5 kN applied at any point. This represents the load that might be exerted by, for example, a glancing blow from a vehicle mirror, a falling branch or malicious interference with the sign. This point load is the critical factor only for very small signs, but for signs mounted on a single support, it causes torsional forces that need to be considered.
For large billboards, live loads and the weight of services should be accounted for the in the design.
Design example
Provide adequate sections for a sign structure with the configuration shown below. The sign post is located in an area that is 76 m above sea level with a wind speed of 35 m/s.
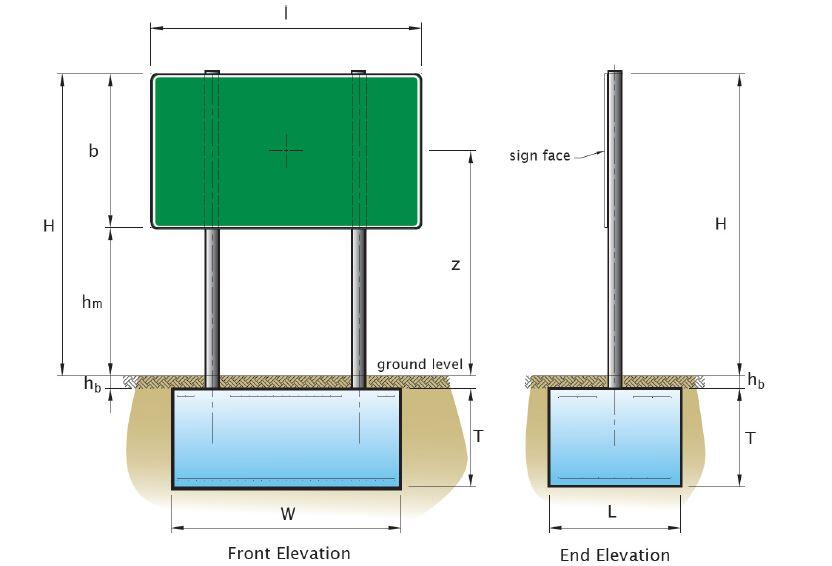
Mounting height above ground hm = 2.0 m
Width of sign face l = 3.0 m
Height of sign face b = 2.0 m
Total height H = hm + b = 4.0 m
Height to centroid of sign area z = hm + b/2 = 3.0 m
Depth of post buried above foundation hb = 200 mm
Basic wind velocity
Let the basic wind velocity from wind map = vb,map = 35 m/s
The altitude of site above sea level A = 76 m
Altitude factor calt = 1 + 0.001A = 1 + (0.001 × 76) = 1.076
vb,0 = vb,map ⋅ calt = 35 × 1.076 = 37.66 m/s
Assess Terrain Orography
Site is not very exposed site on cliff/escarpment or in a site subject to local wind funnelling. Therefore co = 1.0
Determine Design Life Requirement
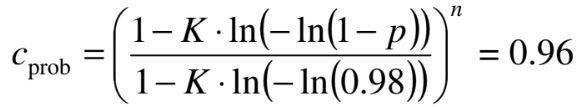
p = design annual probability of exceedence
p = 1/design life = 1/25 = 0.04 (for signs design life is 25 years)
K = Shape parameter = 0.2
n = exponent = 0.5
Basic Wind Velocity
vb = cdir ⋅ cseason ⋅ vb,0
cdir = directional factor = 1.0
cseason = season factor = 1.0
vb = 1.0 × 1.0 × 37.66 = 37.66 m/s
10 minute mean wind velocity having probability P for an annual exceedence is determined by:
vb,25 years = vb ⋅ cprob
vb,25 years = 37.66 × 0.96 = 36.15 m/s
Mean Wind
The mean wind velocity Vm(z) at a height z above the terrain depends on the terrain roughness and orography, and on the basic wind velocity, Vb, and should be determined using the expression below;
Vm(z) = cr(z). co(z).Vb
Where;
cr(z) is the roughness factor (defined below)
co(z) is the orography factor often taken as 1.0
cr(z) = kr. In (z/z0) for zmin ≤ z ≤ zmax
cr(z) = cr.(zmin) for z ≤ zmin
Where:
Z0 is the roughness length
kr is the terrain factor depending on the roughness length Z0 calculated using;
kr = 0.19 (Z0/Z0,II)0.07
Where:
Z0,II = 0.05m (terrain category II)
Zmin is the minimum height = 2 m
z = 3 m
Zmax is to be taken as 200 m
Kr = 0.19 (0.05/0.05)0.07 = 0.19
cr(3) = kr.In (z/z0) = 0.19 × In(3/0.05) = 0.78
Therefore;
Vm(3.0) = cr(z). co(z).Vb = 0.78 × 1.0 × 36.15 = 28.197 m/s
Wind turbulence
The turbulence intensity Iv(z) at height z is defined as the standard deviation of the turbulence divided by the mean wind velocity. The recommended rules for the determination of Iv(z) are given in the expressions below;
Iv(z) = σv/Vm = kl/(c0(z).In (z/z0)) for zmin ≤ z ≤ zmax
Iv(z) = Iv.(zmin) for z ≤ zmin
Where:
kl is the turbulence factor of which the value is provided in the National Annex but the recommended value is 1.0
Co is the orography factor described above
Z0 is the roughness length described above.
For the structure that we are considering, the wind turbulence factor at 3 m above the ground level;
Iv(60) = σv/Vm = k1/[c0(z).In(z/z0)] = 1/[1 × In(3/0.05)] = 0.244
Peak Velocity Pressure
The peak velocity pressure qp(z) at height z is given by the expression below;
qp(z) = [1 + 7.Iv(z)] 1/2.ρ.Vm2(z) = ce(z).qb
Where:
ρ is the air density, which depends on the altitude, temperature, and barometric pressure to be expected in the region during wind storms (recommended value is 1.25kg/m3)
ce(z) is the exposure factor given by;
ce(z) = qp(z)/qb
qb is the basic velocity pressure given by; qb = 0.5.ρ.Vb2
qp(60m) = [1 + 7(0.244)] × 0.5 × 1.25 × 28.1972 = 1345.66 N/m2
Therefore, qp(3m) = 1.345 kN/m2
Determination of force coefficient (Table NA 2 BS EN 12899)
λ = effective slenderness ratio of sign or aspect ratio
λ = l/b = 3.0 / 2.0 = 1.5
Therefore cf = 1.30
Calculation of the total wind force (Clause 5.3 of EN 1991-1-4)
Fw = cscd ⋅ cf ⋅ qp(ze) ⋅ Aref (Aref = area of sign)
cscd = 1.0 (for sign posts)
Fw = 1.0 × 1.30 × 1.345 × 3.0 × 2.0 = 10.5 kN
Partial Factor for Action γF (Table 6 EN 12899-1:2007 (E))
ULS (bending and shear) γF = 1.5
SLS (deflection) γF = 1.0
γf3 = 1.0
Design Wind Force on the sign
Fw,d = Fw ⋅ γF ⋅ γf3
Fw,d (ULS) = 10.5 × 1.5 × 1.0 = 15.75 kN
Fw,d (SLS) = 10.5 × 1.0 × 1.0 = 10.5 kN
Ultimate Action Effects
Ultimate design bending moment per post, MEd
MEd = Wind force × lever arm to foundation / number of posts
MEd = Fw,d (ULS) ⋅ (z + hb) / n
MEd = 15.75 × (3.00 + 0.2) / 2 = 25.2 kNm
Ultimate design shear per post
VEd = Wind force / number of posts
VEd = Fw,d (ULS) /2 = 15.75 / 2 = 7.9 kN
The 0.5 kN point load on the sign is not critical, since it is less than the wind action and there are no torsional effects with 2 posts.
Try circular hollow section CHS 139.7 x 8 (S355)
A = 33.1 cm2; Wpl = 139 cm3; Ix = 720 cm4
Section classification
ε = √235/fy = √(235/355) = 0.81
Tubular sections (Table 5.2, sheet 3 of EN 1993-1-1:2005):
d/t = 139.7/8 = 17.46
Limit for Class 1 section = 50ε2 = 40.7
40.7 > 17.46; section is Class 1
Member resistance at ULS
According to Table 7 of EN 12899-1:2007 (E), the material factor of safety for steel is γm = 1.05
Moment Capacity MRd = fy⋅Wpl/γm = [(355 x 103 x 139 x 10-6)/√3)]/1.05= 46.99 kNm
MEd/MRd = 25.2/46.99 = 0.536 < 1.0 Okay
Shear capacity VRd = Av(fy/√3)/γm
Av = 2A/π = (2 x 33.1)/π = 21.027 cm2
VRd = 21.027 × 10-4 × [(355 x 103)/√3)]/1.05 = 430.96 kN
VEd/VRd = 7.9/430.96 = 0.018 < 1.0 Okay
Calculation of Temporary deflection
The wind velocity for calculating the temporary deflection (SLS) criterion is 75% of the reference wind velocity, as it is based upon a 1 year mean return period. The 0.96 factor below reverses the cprob conversion from 50 to 25 year return period used above (Clause 5.4.1, note 1 EN 12899-1).
Fwd(1 year) = Fwd (SLS) x 0.752/0.962 = 10.5 x 0.752/0.962 = 6.41 kN
Uniformly distributed load along sign face = Fw,d (1 year) / b
Fw,d (1 year) / b = 6.41/2.0 = 3.2 kN/m
where b = height of the sign face
Maximum deflection at top of sign (bending), δ
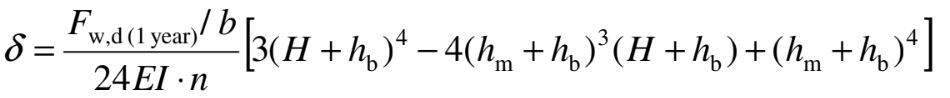
E = 210000 N/mm2
I = 720 cm4
n = number of posts = 2
Other parameters are as defined above
δ = [3.2/(24 x 210000 x 720 x 104 x 2)] x [3(4000 + 200)4 – 4(2000 + 200)3 x (4000 + 200) + (2000 + 200)4] = 34.3 mm
Deflection per linear metre = δ’ = δ/(H + hb) = 34.3/(4 + 0.2)= 8.16 mm/m
Maximum temporary deflection taken as class TDB4 = 25 mm/m
8.16 mm/m < 25 mm/m. Therefore deflection is okay.
References
The Institution of Highway Engineers (2010): SIGN STRUCTURES GUIDE Support design for permanent UK traffic signs to BS EN 12899-1:2007 and structural Eurocodes









This calculation is very well explained! It would be nice if you also have a FEM analysis.
This calculation is very well explained! It would be nice if you also have a FEM analysis