Modern codes of practice are increasingly recognising the computational power of structural analysis softwares. Staad Pro is a renowned structural analysis and design software that is used all over the world, and this post is aimed at investigating the analysis of beam and raft foundation using Staad Pro V8i. Winkler’s model has been used as a basis for the analysis. This post will help engineers who use Staad Pro to make decisions on whether raft slab can be confidently analysed on Staad Pro V8i environment, or there will be need to move to Staad Foundation, or any other foundation analysis software.
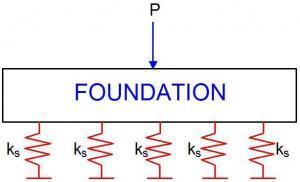 |
| Fig 1: Winkler’s Model |
Winkler’s model assumes that soil possesses stiffness which is considered to be the ratio of the contact pressure of the soil, and the vertical deformation associated with it. This relationship is assumed to be linear, and can be given by what is called the coefficient of subgrade reaction (ks).
ks = q/S ——————- (1)
where;
q is the contact pressure at a point in the footing, and
S is the settlement at the same point.
Equation (1) assumes that for granular soils, the value of ks is independent of the magnitude of pressure, and is the same at all points on the surface of the footing. These two assumptions are however not very accurate for obvious reasons, especially for flexible foundations. There are lots of literature available on the topic of ‘coefficient of subgrade reaction’, and you are advised to read them up on Google. However, it is accepted that the method gives realistic contact pressures especially when considering very low order of settlement. Coefficient of subgrade reaction is obtained in the field using in-situ plate load test. Plate load tests are usually carried out using (300 x 300) mm plate, and there is usually need to correct the obtained value for the actual width of the foundation (for a quick check of procedure, see page 696 of Murthy, 2012). I will not actually dabble into the accuracy of application of coefficient of subgrade reaction for foundation design in this post, but the reader is advised to consult wide range of literature since opinion on this seems to vary.
In Staad Pro software, the use of Winkler’s Model can easily be done by applying ‘foundation’ support option to the structure in question. Under this option, you can use ‘elastic mat’ or ‘plate mat’. Elastic mat is suitable for beam and plate combination (e.g beam and raft slab in a building) while plate mat is good when you have plate elements only forming the base (e.g base of an underground water tank). For training on how to use Staad Pro efficiently, contact the author on ubani@structville.com
In many parts of Nigeria, beam and raft slab is employed for low-medium rise buildings when the soil has low bearing capacity (usually between 100 kPa and 50kPa) or where providing separate bases will pose so many challenges. For manual analysis of such foundations, the rigid approach is usually used, which yields higher value of internal stresses, while on the other hand, finite element based foundation design softwares can be used, which usually yields lower internal stresses but higher settlement (flexible approach).
In the design of beam and raft slab foundation, it is usually assumed that the column load gets transferred/distributed to the ground beams, and tries to push them down into the soil. This action is resisted by the earth pressure intensity, which is mainly transferred to the ground floor slab. The schematic diagram of this action is shown below.
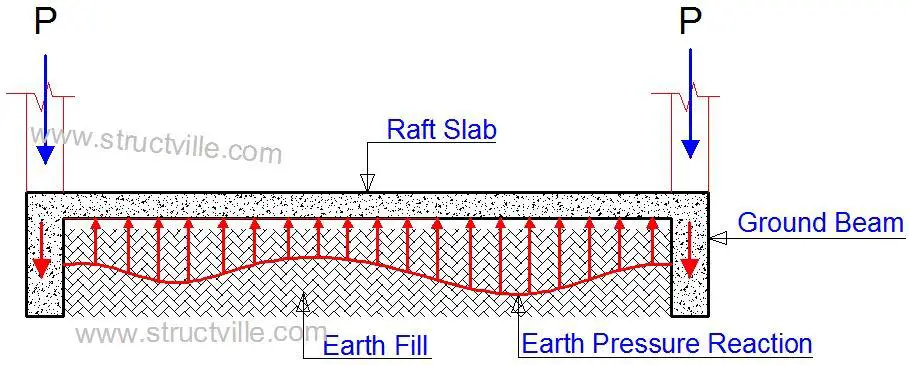 |
| Fig 2: Load Path of Beam and Raft Foundation |
Design Example
As an example, let us consider a two storey building with the foundation layout shown below.
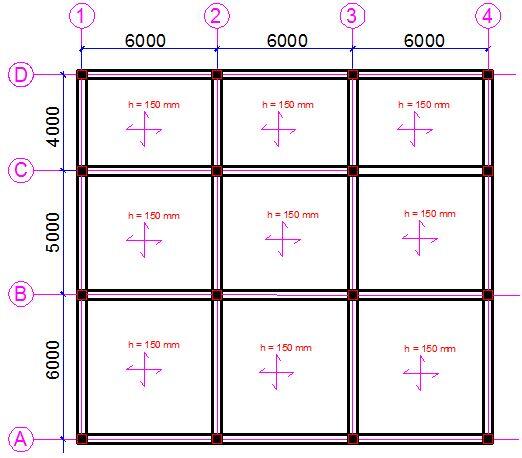 |
| Fig 3: Typical Foundation Layout of Structure |
For the beam and raft layout shown in Fig. 3, the necessary data are as follows;
Ground beam dimensions = 1200 x 250 mm
Thickness of ground floor slab = 150 mm
Dimension of all columns = 230 x 230 mm
First floor slab = 150 mm
First floor beams = 450 x 230 mm
Roof beams = 300 x 230 mm
Additional dead load on floors (finishes and partition allowance) = 2 kN/m2
Imposed load on building (variable action) = 2 kN/m2
Load at ultimate limit state = 1.35gk + 1.5qk
Coefficient of subgrade reaction ks = of 20000 kN/m2/m (assumed for very soft clay, reference taken from CSC Orion Software)
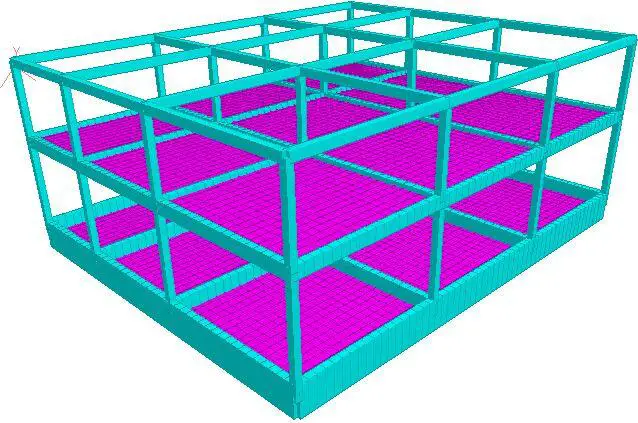
The 3D view of the frame is shown in Figure 4 below;
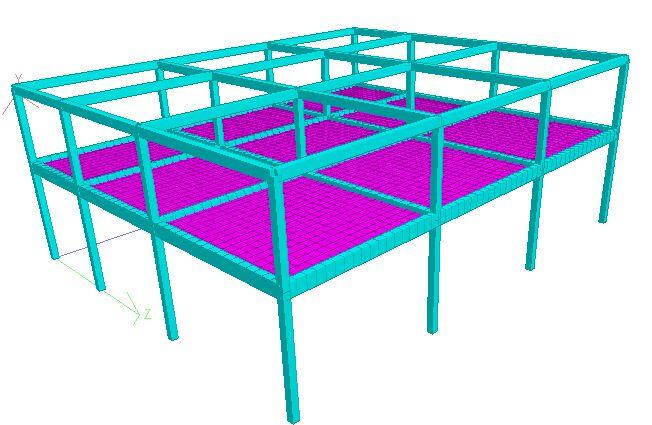 |
| Fig 4: 3D Model of the Building |
After analysis of the superstructure on Staad, the following ultimate column axial loads which are transferred to the foundation are shown below;
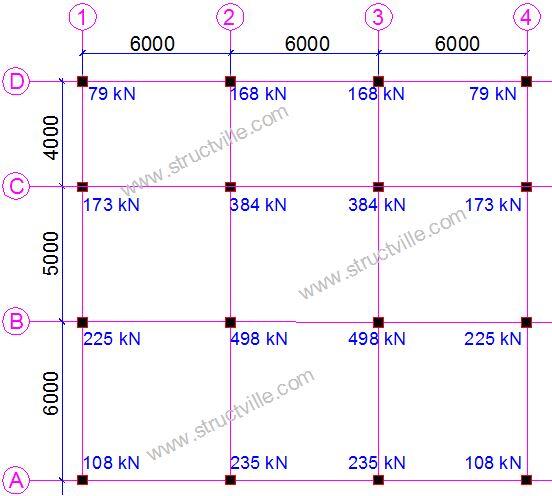 |
| Fig 5: Column Loads on the Foundation |
From figure 5 above, I believe you can easily model the foundation in another software, or carry out manual analysis for checks of the procedure adopted here.
When the ground beams and elastic mat foundations are applied on Staad Pro, the results are as follows;
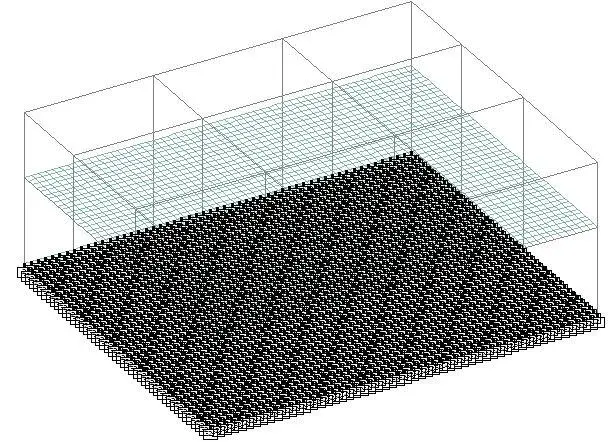 |
| Fig. 6: Typical View of the Structure with Elastic Mat Foundation |
(1) Base Pressure
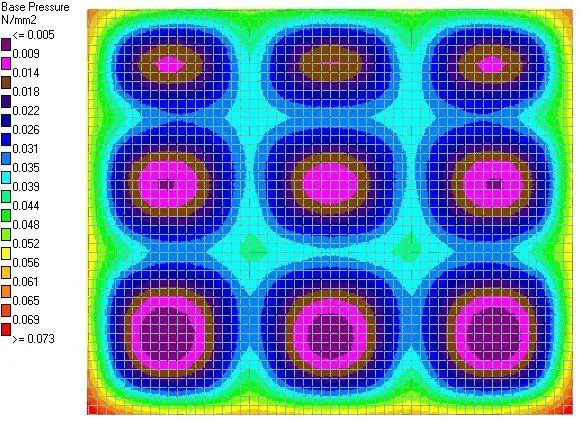 |
| Fig. 7: Base Pressure |
A little consideration will show that we are obtaining a maximum base pressure of 73 kPa at the edges, which might be higher than the bearing capacity of the soil. The engineer is advised to review this properly. However, along grid lines 2 and 3, we have base pressure of 39 kPa which increases towards the edges. The minimum base pressure occurred at the mid-spans.
(2) Moment in the raft slab (x-direction)
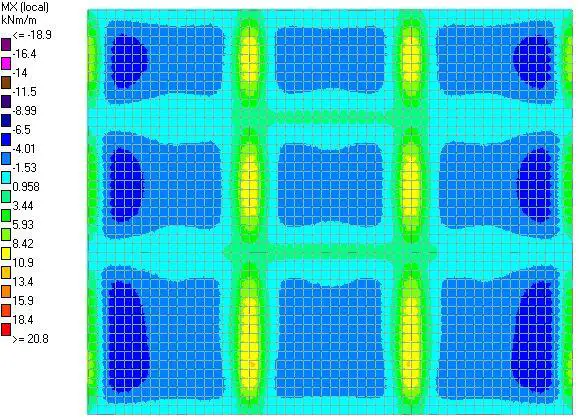 |
| Fig 8: Mx Moment |
The bending moment on the raft slab was discovered to be low when compared with the value that could be gotten using the rigid approach (the maximum moment can be seen to be within 10.9 and 13.4 kNm/m)
(3) Bending moment in the Y-direction
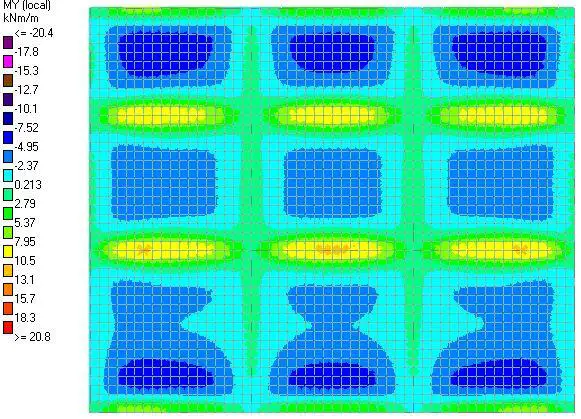 |
| Fig 9: My Moment |
(4) Twisting Moment
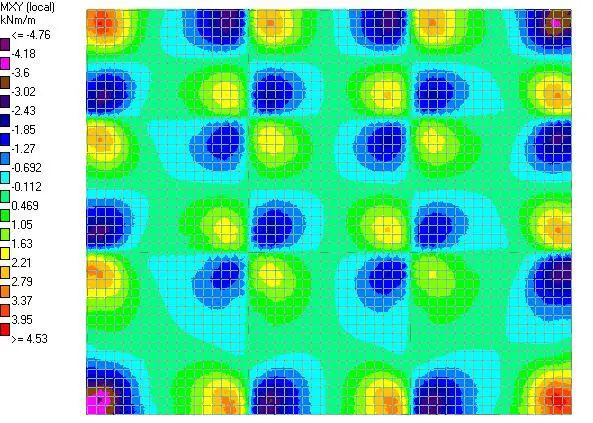 |
| Fig 10: Mxy Moment |
(5) Bending Moment in the ground beams
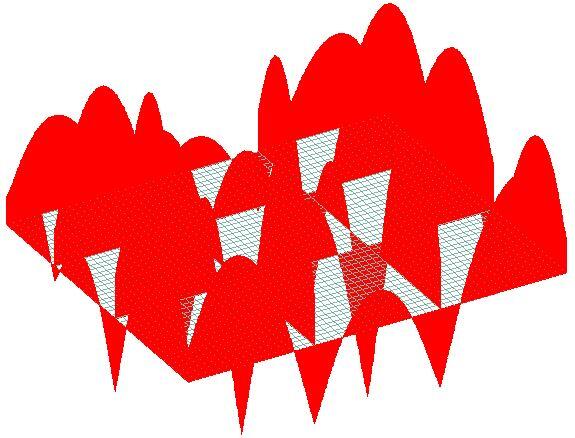 |
| Fig 11: Bending Moment Diagram of the Ground Beams |
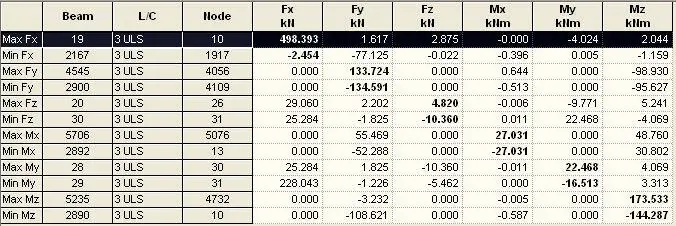
For simplicity, the maximum design forces have been presented in the table below;
The bending moment on ground beam of grid line (2) is given below;
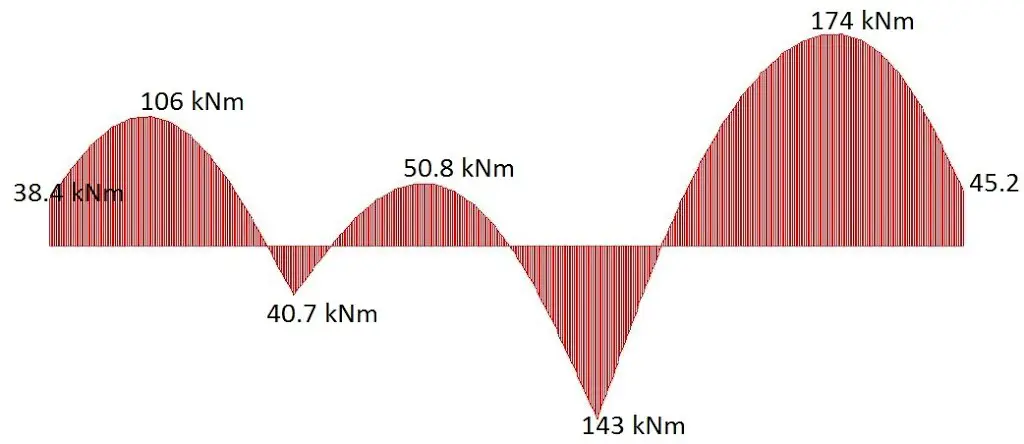 |
| Fig 12: Bending Moment for Ground Beam Grid line 2 |
What are your thoughts on the values obtained? At your convenience, you can model the raft slab on the software you normally use, and compare the results obtained. You can present your observations in the comment section for review.
Thank you for visiting Structville, and God bless you.
Citation
Murthy V.N.S (2012): Textbook of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering (Geotechnical Engineering Series) 1st Edition. CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd, India ISBN: 81-239-162-1